Home / Training / Manuals / Atlas of breast cancer early detection / Cases
Atlas of breast cancer early detection
Go back to the list of case studies
.png) Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
Click on the pictures to magnify and display the legends
| Case number: | 024 |
| Age: | 39 |
| Clinical presentation: | Premenopausal woman with average risk of developing breast cancer presented with a long-standing breast lump in the left breast. Examination revealed a large (8 × 9 cm), lobulated, firm, and mobile lump that occupied all the quadrants in the left breast. |
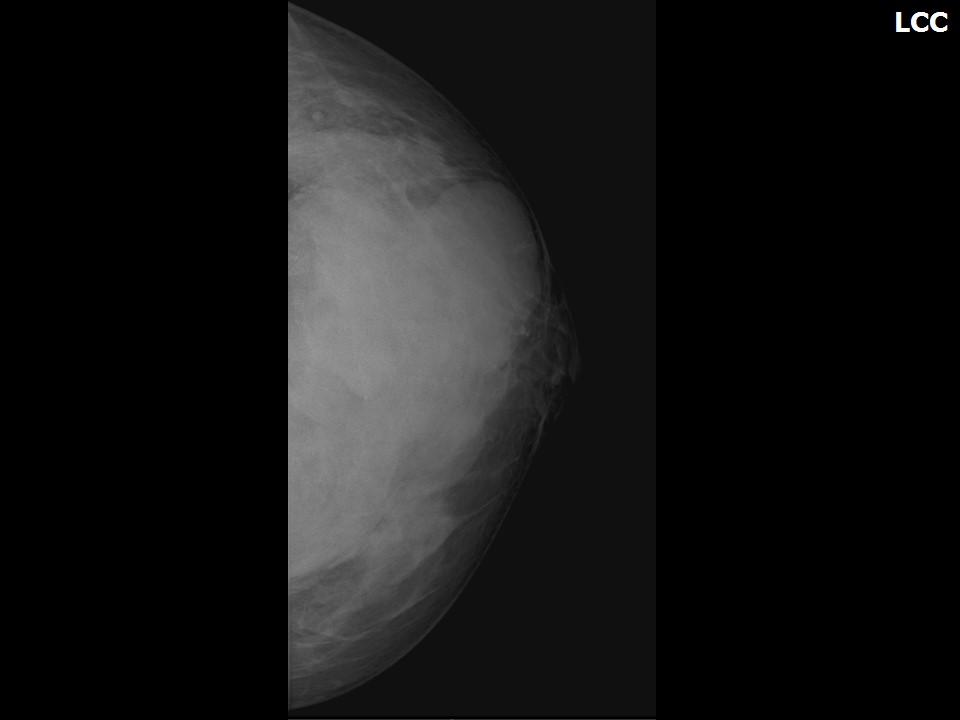
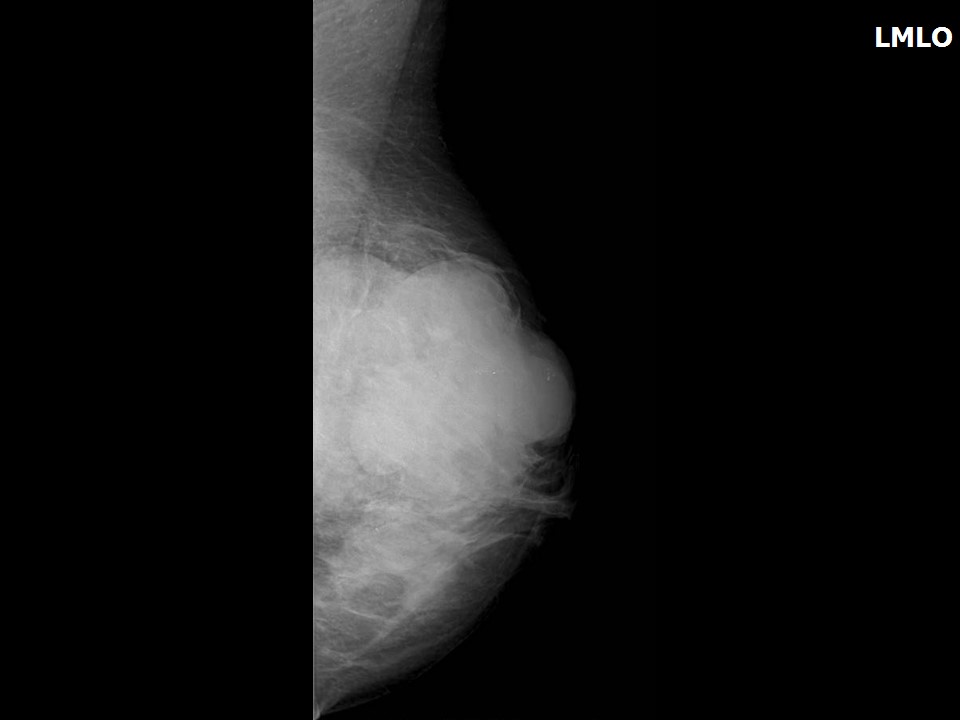
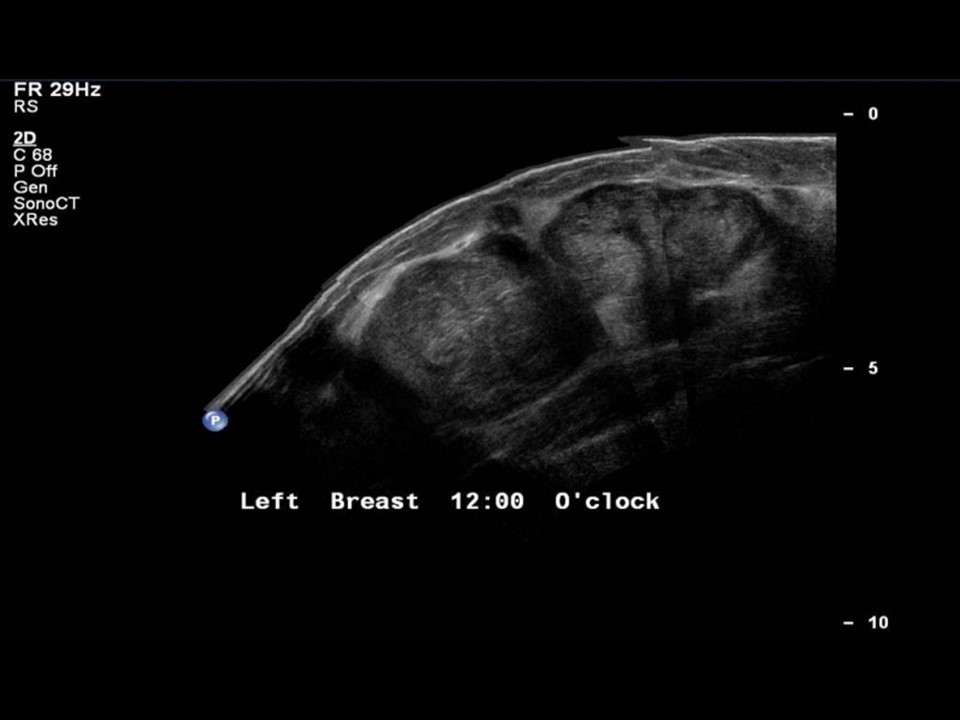
Mammography:
| Breast composition: | ACR category c (the breasts are heterogeneously dense, which may obscure small masses) | Mammography features: |
| ‣ Location of the lesion: | Left breast, upper quadrants at 11–2 o’clock, anterior, middle, and posterior thirds |
| ‣ Mass: | |
| • Number: | 1 |
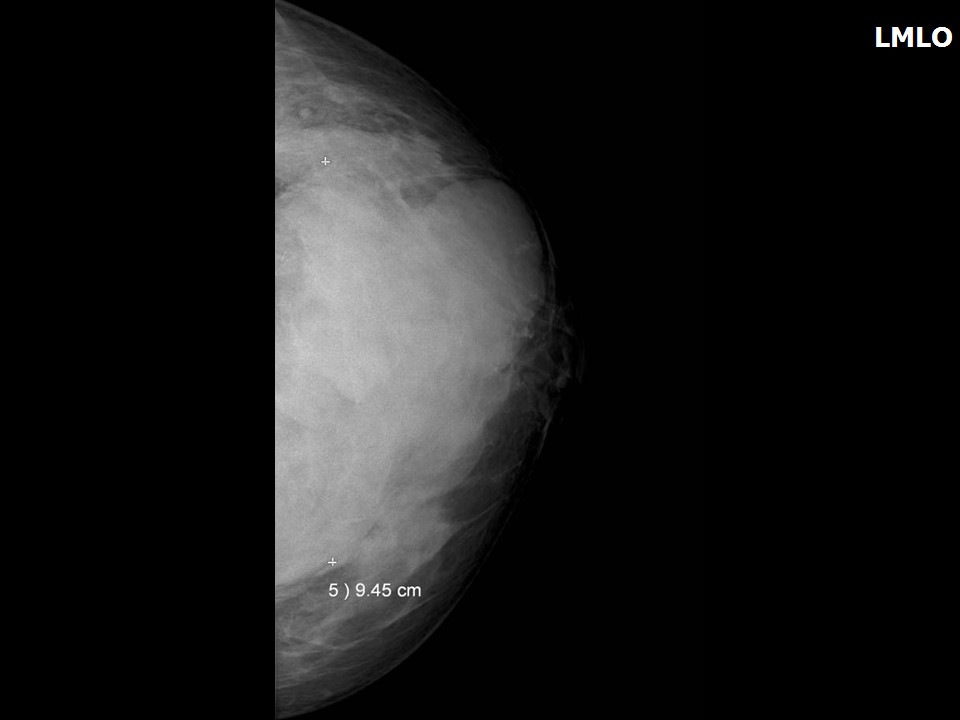
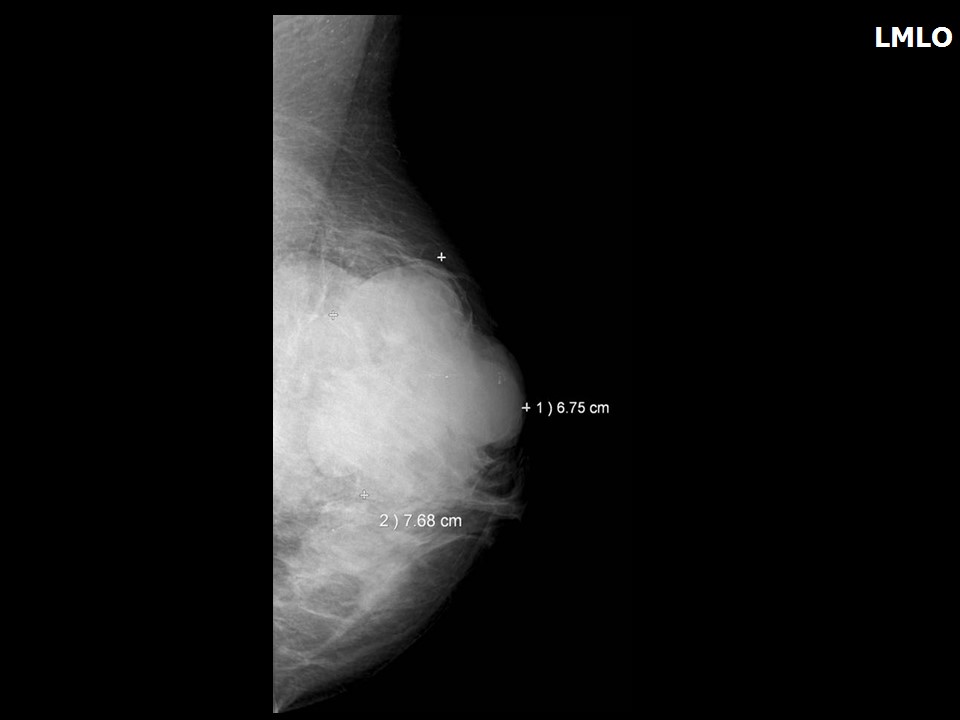
| • Size: | 9.5 × 8.0 × 7.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Irregular |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed with perilesional halo and splaying of adjacent fibroglandular tissues |
| • Density: | Equal |
| ‣ Calcifications: | |
| • Typically benign: | None |
| • Suspicious: | None |
| • Distribution: | None |
| ‣ Architectural distortion: | Present |
| ‣ Asymmetry: | Global |
| ‣ Intramammary node: | None |
| ‣ Skin lesion: | None |
| ‣ Solitary dilated duct: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Architectural distortion |
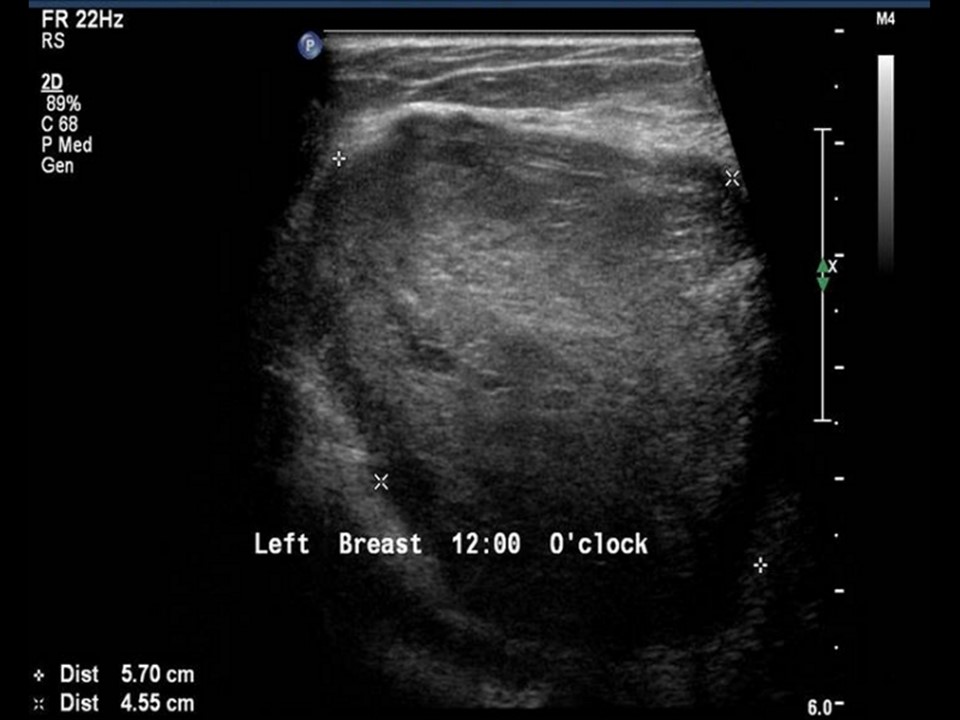
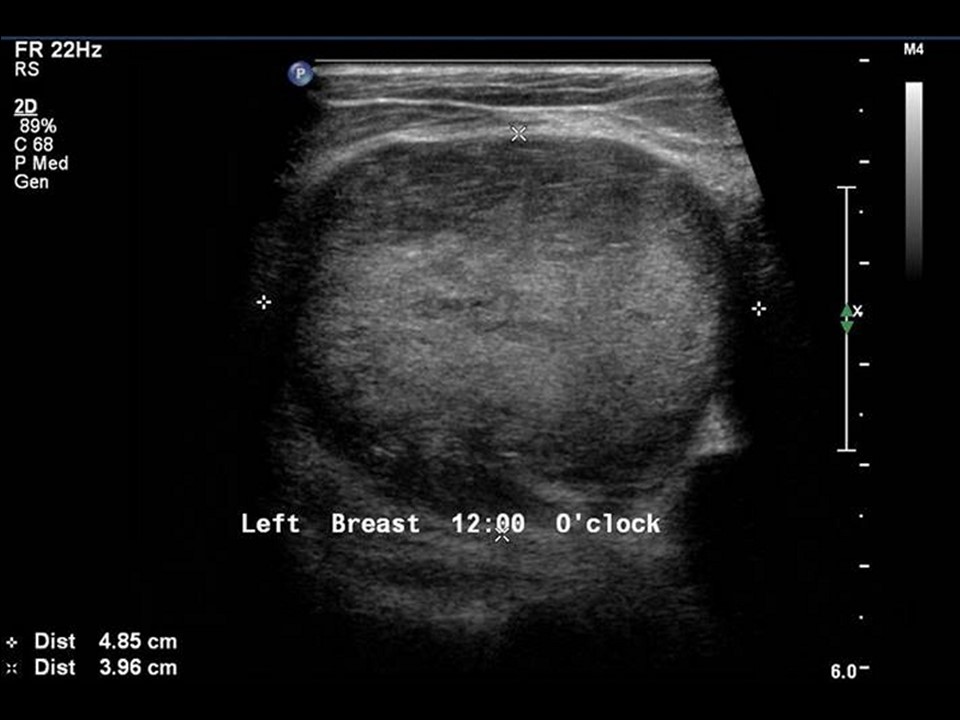
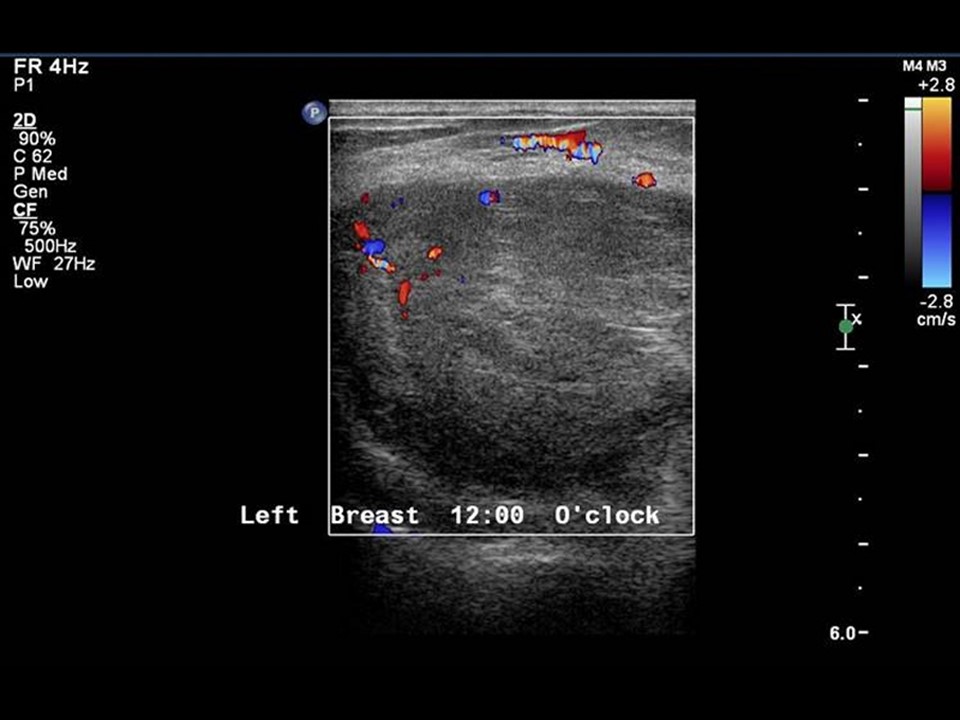
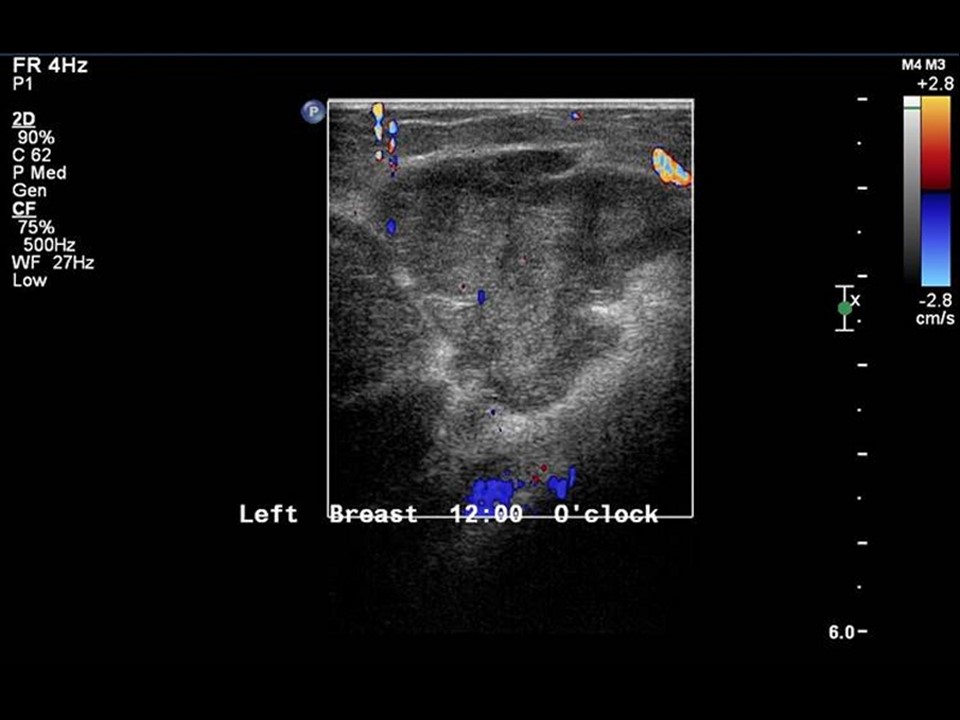
Ultrasound:
| Ultrasound features: Left breast, upper quadrants at 11-2 o'clock | |
| ‣ Mass | |
| • Location: | Left breast, upper quadrants at 11-2 o'clock |
| • Number: | 2 |
| • Size: | Largest 6.0 × 5.0 cm and another 5.0 × 4.0 cm |
| • Shape: | Oval |
| • Orientation: | Parallel |
| • Margins: | Circumscribed |
| • Echo pattern: | Hypoechoic |
| • Posterior features: | No posterior features |
| ‣ Calcifications: | None |
| ‣ Associated features: | Internal vascularity |
| ‣ Special cases: | None |
BI-RADS:
BI-RADS Category: 4A (low level of suspicion for malignancy)Further assessment:
Further assessment advised: Referral for cytologyCytology:
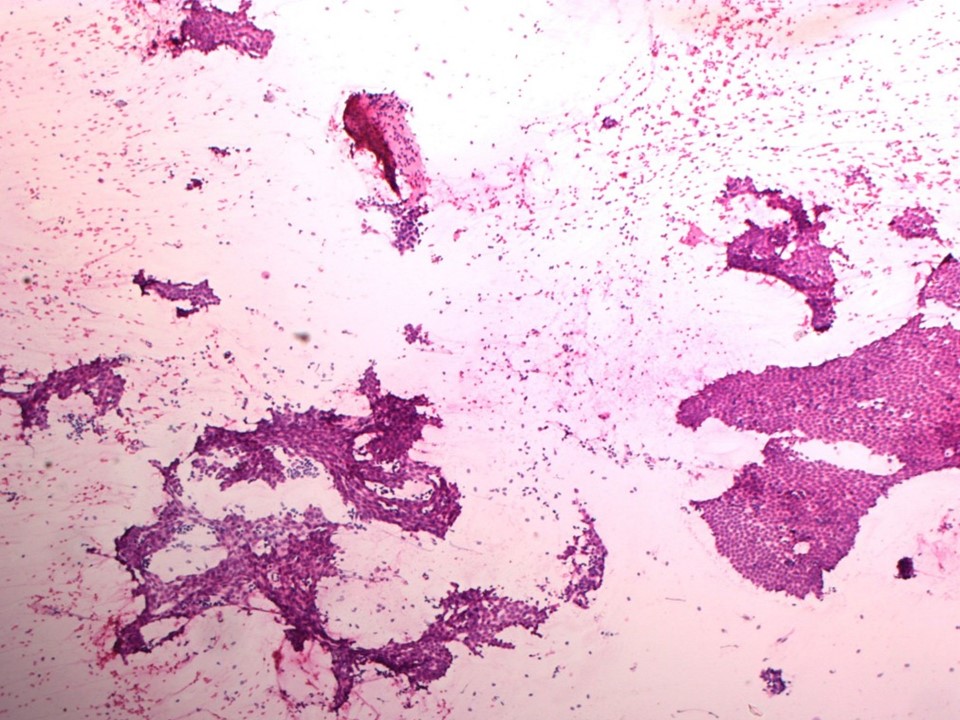
| Cytology features: | |
| ‣ Type of sample: | FNAC |
| ‣ Site of biopsy: | |
| • Laterality: | Left |
| • Quadrant: | |
| • Localization technique: | Palpation |
| • Nature of aspirate: | Whitish |
| ‣ Cytological description: | Smears are very cellular with many tightly cohesive sheets of benign ductal epithelial cells. Plenty of bare nuclei are seen in the background. Very few stromal fragments are seen |
| ‣ Reporting category: | Benign |
| ‣ Diagnosis: | Fibroadenoma |
| ‣ Comments: | None |
Histopathology:
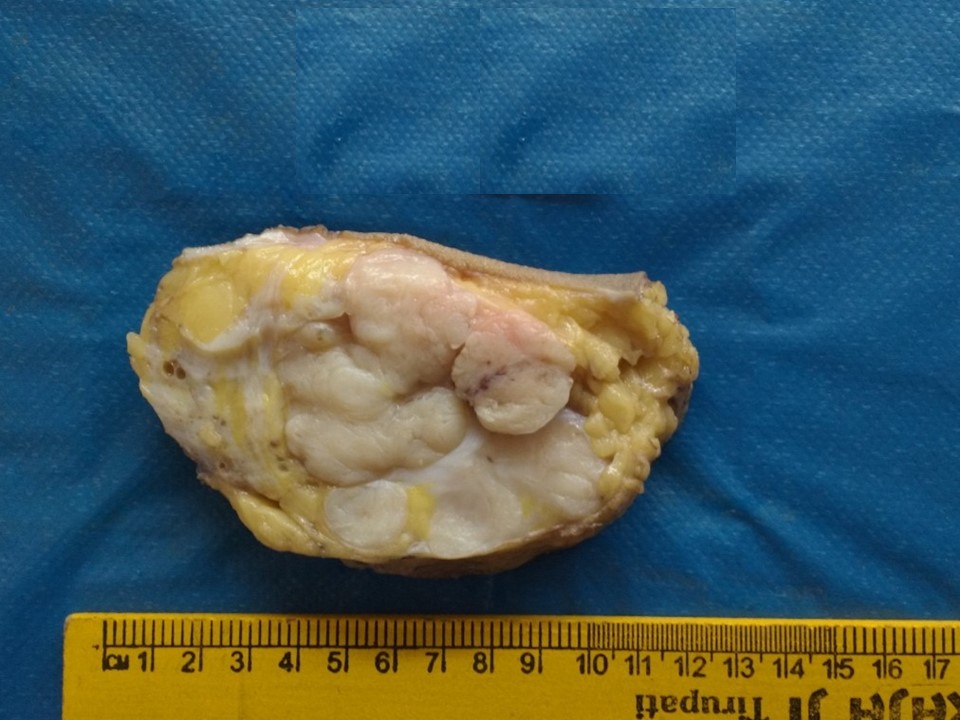
Simple mastectomy
| Histopathology features: | |
| ‣ Specimen type: | Simple mastectomy |
| ‣ Laterality: | Left |
| ‣ Macroscopy: | Specimen (15 × 13 × 6.0 cm) with overlying skin flap (11.5 × 10.0 cm). The nipple and areola are unremarkable. On serial sectioning, a well-circumscribed lobulated multinodular bulging mass (9.0 × 7.0 × 6.5 cm) is identified with focal areas of cystic changes and cleft-like areas located 0.3 cm from the skin, 1.2 cm from the superior margin, 2.5 cm from the inferior margin, 0.8 cm from the medial margin, and 1.2 cm from lateral margins and flushing the base grossly. Medial and inferior to the larger lump is a whitish, nodular, well-circumscribed mass (1.0 × 1.5 × 1.3 cm). It is 1.0 cm below the larger mass. The remaining breast shows areas of fibrosis and cystic change |
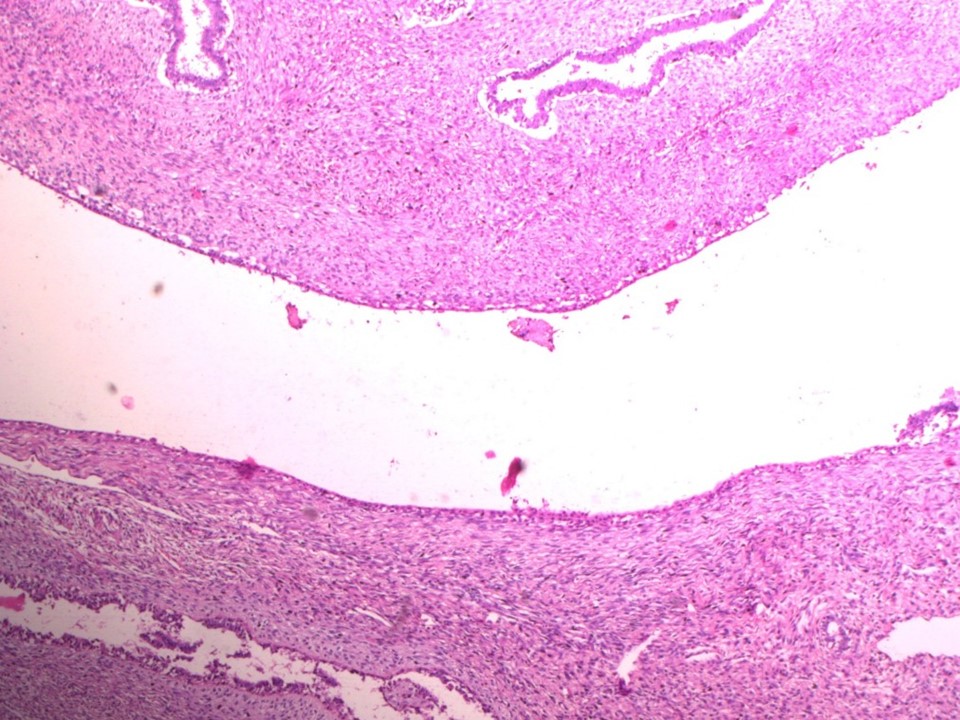
| ‣ Histological type: | Sections from the left breast lump reveal proliferation of glands and stroma. The stroma is hypercellular and shows many spindle cells that are uniform and show minimal atypia. No areas of necrosis are seen. The glands show areas of epithelial hyperplasia. A second, smaller, firm area shows features of fibroadenoma |
| ‣ Histological grade: | |
| ‣ Mitosis: | 2 |
| ‣ Maximum invasive tumour size: | |
| ‣ Lymph node status: | |
| ‣ Peritumoural lymphovascular invasion: | |
| ‣ DCIS/EIC: | |
| ‣ Margins: | Free of tumour |
| ‣ Pathological stage: | |
| ‣ Biomarkers: | |
| ‣ Comments: |
Case summary:
| Premenopausal woman presented with a left breast lump of long duration. Diagnosed as a large circumscribed mass in the left breast, BI-RADS 4A on imaging, as fibroadenoma on cytology, and as phyllodes tumour on histopathology. |
Learning points:
|